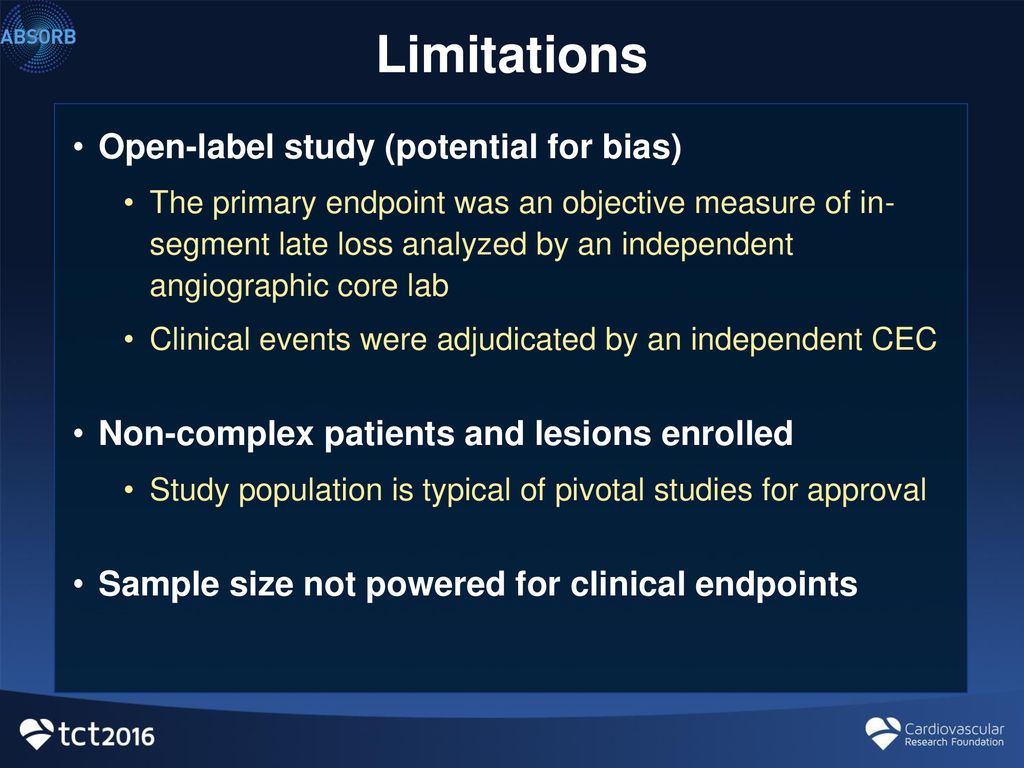
41 open-label study bias
PDF What Are Open-Label Extension Studies For? - The Journal of Rheumatology factors. In the case of open-label extension studies, we feel that analysis of efficacy ought to regard treatment allocation as a possible explanatory variable (in addition to others, such as baseline status and time). The study by Mease and colleagues 1 reports the results of a 48-week open-label extension of a 24-week randomized Impact of open-label versus blinded study design on patient-reported ... Aim A systematic literature review of immuno-oncology trials was conducted to assess the potential impact of open-label vs double-blind trial design on patient-reported outcome (PRO) data. Methods A systematic search of indexed literature published from January 2009 to May 2019 was conducted using PubMed/MEDLINE, Cochrane Library, and EMBASE database. All randomized clinical trials (RCTs) of ...
FDA Guidance: "Design Considerations for Pivotal Clinical ... •Bias and Variance •Study Objectives ... - For non-masked (open label) studies this means before any patient reaches an outcome. 36. Closing Remarks

Open-label study bias
Open-Label Trial - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics They may be informed of this opportunity before or after the double-blind trial (or whatever study precedes the open-label extension study). Such studies can generate long-term data on the intervention's efficacy, safety, and administration. ... Blinding the researchers as well as the patients helps minimize experimenter's bias. Double-blinds ... Some Blinding Techniques in Clinical Trials - Blogger The firewall between the sponsor the investigator/clinical research organization can also be implemented in an open label study or single-blind study so that the sponsor is prevented to access the cumulative data for the primary efficacy endpoint for analysis. ... Brennan C Kahan (2014) Reducing bias in open-label trials where blinded outcome ... (PDF) Reducing bias in open-label trials where blinded outcome ... Regarding study design, there was also agreement that the risk of bias associated with unblinding TSs was likely to be smaller for open-label trials, where the nature of the treatments under ...
Open-label study bias. Exploring open-label bias in patient-reported outcome (PRO) emotional ... e18702 Background: Concern exists that patients' self-reports may be biased in open-label trial designs. We compared PRO emotional domain results between investigational arms of paired open label and double-blind trials of the same drug and disease population. We hypothesized that greater improvement in emotional domain scores would be found in the investigational arms of open label compared ... (PDF) What is an open label trial? - ResearchGate An open label randomised controlled trial study design was used. The control treatment was prazosin alone. The setting was a hospital and research centre in Mahad, a region of India.... External and internal validity of open label or double‐blind trials in ... Naturally, in open-label trials in anticoagulation there is a risk of a reporting bias of adverse events. Patients may research the new drug and its side-effects in publications and may be influenced in their reporting behaviour of potential side-effects. Furthermore, investigators may be equally susceptible to a reporting bias. Placebos and Blinding in Randomized Controlled Cancer Clinical Trials ... In open-label comparative trials for which investigator bias may be of concern, a blinded central independent review of scans may mitigate bias regarding endpoint assessment.
Open-label extension studies: do they provide meaningful ... - PubMed Some increased confidence about incidence rates might result from the open-label extension study; however, as these studies are essentially uncontrolled and biased, the data are not of great value. Other benefits have been proposed to be gained from open-label extension studies. Open-label placebos—a systematic review and meta-analysis of ... The use of open-label placebos (OLPs) has shown to be effective in clinical trials. ... one study was rated as having a high risk of bias. This study showed the largest effect size of all studies ... Reducing bias in open-label trials where blinded outcome assessment is ... Many trial designs do not permit blinding, and are therefore designed as open-label, with patients, clinicians, and other study investigators aware of treatment allocation. Research has suggested that these trials should use blinded outcome assessment to avoid bias in estimated treatment effects [ 6 - 10 ]. Statistical controversies in clinical research: limitations of open ... Estimation bias of the treatment effect was determined by the ratio of OR, by dividing the OR values obtained in open-label trials by those obtained in DB trials. Results The literature-based meta-analysis included 166 trials (72 024 patients).
Understanding Clinical Trial Terminology: What is an Open Label ... Alternatively, sometimes, trials are conducted in an open-label fashion, meaning study participants and researchers both know which treatment the patient is receiving. Open-label trials can be used to compare treatments or gather additional information about the long-term effects in the intended patient population. Design characteristics, risk of bias, and reporting of randomised ... Open label trials were not automatically at high risk of bias owing to deviations from intended interventions; similarly, trials with blinding were not immune to bias by default. Statistical controversies in clinical research: limitations of open ... However, the bias apparently concerns open-label as well as DB trials, suggesting that asymmetry was not related to the design of the missing trials. Analysis by study design showed an OR for bleeding of 3.18 (95% CI 2.65-3.81) for open-label studies and 1.89 (95% CI 1.63-2.19) for DB studies (Figure 2). The ratio of these two ORs ... What is an Open-Label Clinical Trial? - News-Medical.net Open-label trials can be used to gather additional safety and efficacious data on drugs on the market to increase the confidence of clinicians, patients, and clinical bodies. They can play a key...
Effects of open-label placebos in clinical trials: a ... - Nature Open-label placebos (OLPs) are placebos without deception in the sense that patients know that they are receiving a placebo. The objective of our study is to systematically review and analyze...
8.4 Introduction to sources of bias in clinical trials - Cochrane Detection bias refers to systematic differences between groups in how outcomes are determined. Blinding (or masking) of outcome assessors may reduce the risk that knowledge of which intervention was received, rather than the intervention itself, affects outcome measurement.
What is an open label trial? | The BMJ An open label randomised controlled trial study design was used. The control treatment was prazosin alone. The setting was a hospital and research centre in Mahad, a region of India. Participants were patients with grade 2 scorpion envenomation, older than 6 months, and with no cardiorespiratory or central nervous system abnormalities.
Investigating the impact of open label design on patient‐reported ... Bias may occur in open-label trials, as observer bias and disappointment bias. 34 - 37 Therefore, according to the FDA, patients may be prone to provide biased reports of their own symptoms if they are aware of the treatment they received and lead to an overestimation of the treatment difference observed between the two treatment arms.
Lack of blinding - Catalog of Bias The lack of concealment of an intervention or control treatment received by participants in a clinical trial. Background The aim of blinding is to reduce bias due to the knowledge of which intervention or control is being received by study participants.
A potential bias in safety evaluation during open-label ... - PubMed A potential bias in safety evaluation during open-label extensions of randomized clinical trials The confounding described here is not prevented by randomization because it develops in a non-randomized add-on analysis to the trial. The bias can be removed, however, by controlling for time since randomization in the analysis of the data.
(PDF) Reducing bias in open-label trials where blinded outcome ... Regarding study design, there was also agreement that the risk of bias associated with unblinding TSs was likely to be smaller for open-label trials, where the nature of the treatments under ...
Some Blinding Techniques in Clinical Trials - Blogger The firewall between the sponsor the investigator/clinical research organization can also be implemented in an open label study or single-blind study so that the sponsor is prevented to access the cumulative data for the primary efficacy endpoint for analysis. ... Brennan C Kahan (2014) Reducing bias in open-label trials where blinded outcome ...
Open-Label Trial - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics They may be informed of this opportunity before or after the double-blind trial (or whatever study precedes the open-label extension study). Such studies can generate long-term data on the intervention's efficacy, safety, and administration. ... Blinding the researchers as well as the patients helps minimize experimenter's bias. Double-blinds ...






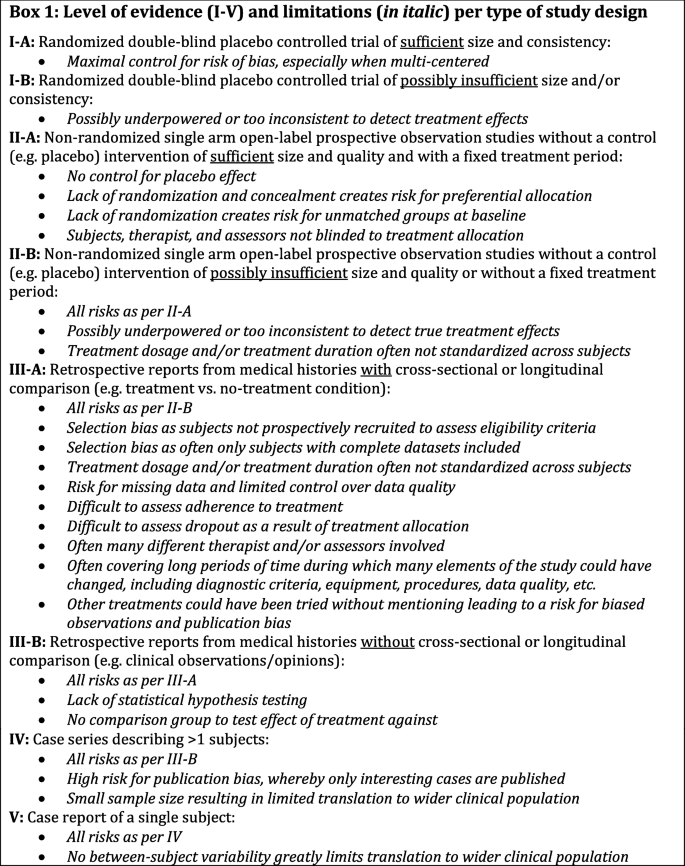



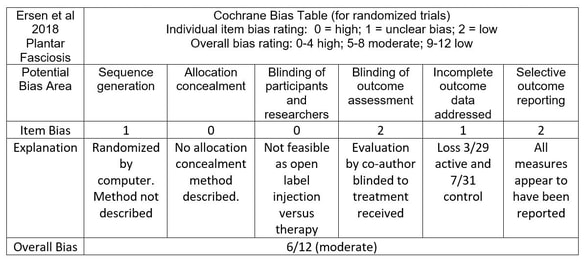
![PDF] The Clinical Viewpoint: Definitions, Limitations of ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/0d341492d445073e64d1ccb6985e4ad763a3d1f7/2-Table1-1.png)













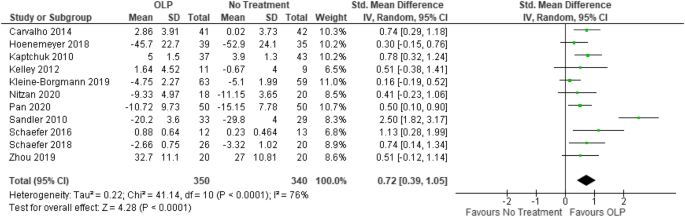
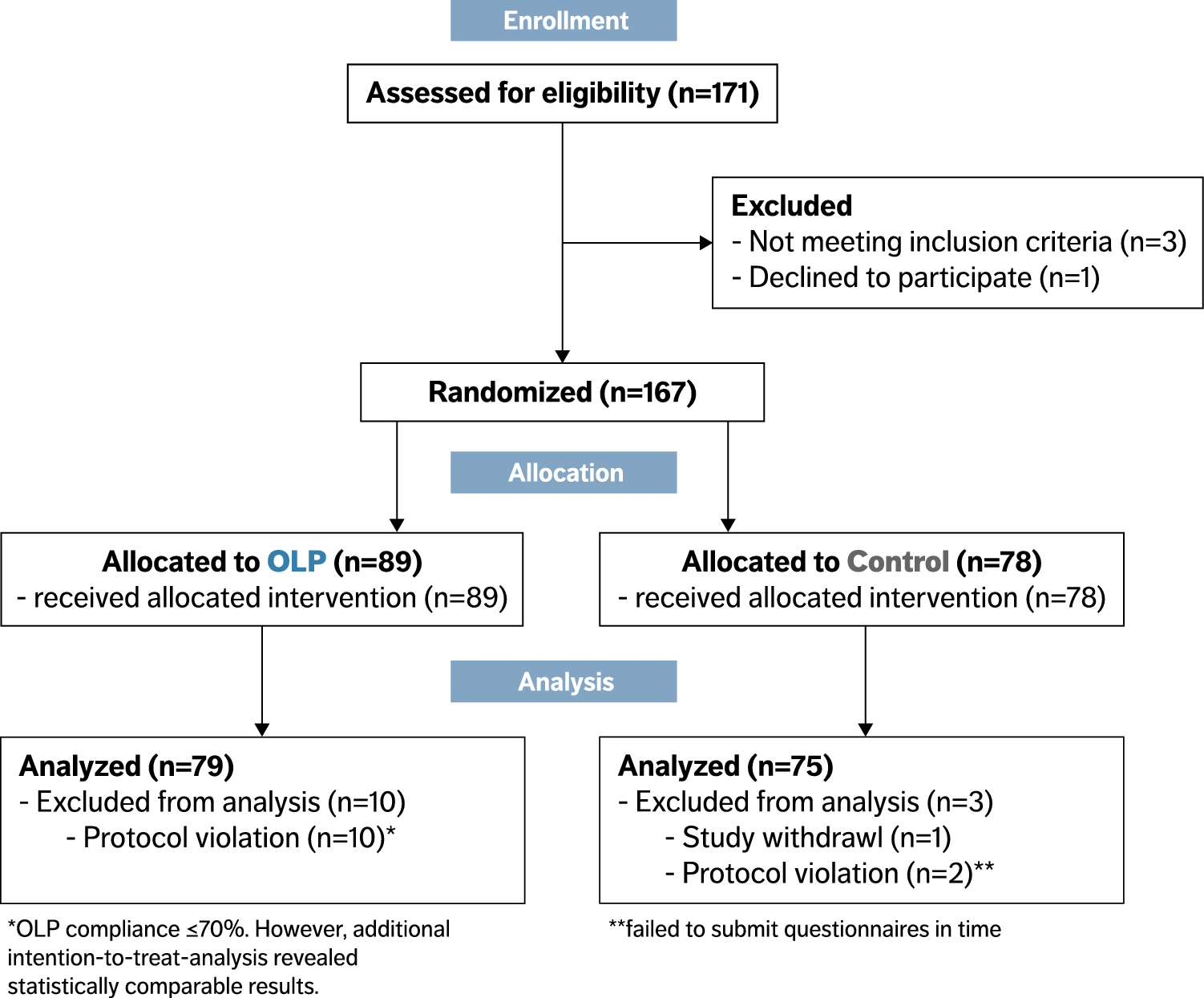
![PDF] Bias was reduced in an open-label trial through the ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/814ad6ccbfa9defca4d2b00c4672f9070cf6b8da/16-Figure1-1.png)

Post a Comment for "41 open-label study bias"